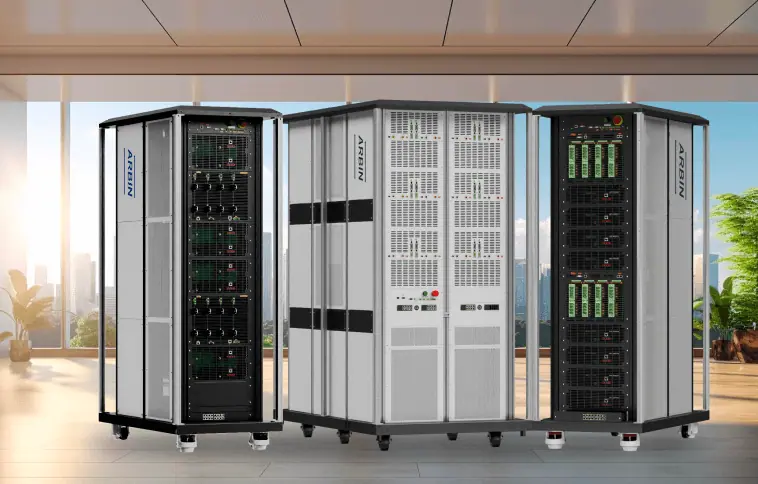
Battery Test Equipment
Arbin products delivers fast, accurate Self-Discharge Current measurement while maintaining battery electrochemical balance. Our technology allows the applied small current to be constant and unaffected by temperature changes, ensuring precision throughout the process.
Battery R&D Equipment
Arbin's range of research and development testing solutions ensures researchers have the tools needed to bring new technology to the market.
Cell, Module & Pack Tester
For decades, Arbin's equipment has defined industry standards, helping our customers to confidently advance energy storage innovation.
Software Solutions
Our Cross Platform MITS Software provide comprehensive, reliable data, that fulfill those needs.
Arbin offers charge/discharge battery testing systems
ranging from μA single cell applications up to 1MW packs.
Cutting-edge technology and an innovative alternative to the traditional ACIM technique for measuring battery impedance, uses Galvanostatic and AI Prediction Modeling Methods provide distinct advantages without additional equipment is required, shorter test times, and it maintains accuracy comparable to ACIM.


SDCM is essential for evaluating a battery's state of health, predicting its performance, and estimating its lifespan. We have revolutionized this method, making it significantly faster and more accurate while lowering equipment requirements.
Arbin applies this structure into several applications

Battery Energy Storage System
Applications Include
- Coincell, cylindrical, prismatic, & pouch/flat cell testing
- Battery modules and packs of all sizes
- Any battery chemistry including lithium, silicon, sulfur, lead-acid, nickel, & more
- Battery cycling, electrochemical experiments, and advanced real-world simulations
- HPC measurements (coulombic efficiency)
- Electric vehicle battery testing

Highlight Products
High Precision Tester (HPS)
With integrated chambers, HPS offers a turn-key solution with state-of-the-art technology for battery research, ensuring unmatched accuracy and precision.
Parallel Differential Battery Tester (PDBT)
PDBT is designed for battery parallel test for battery comparison and fast self-discharge current measurement.
Laboratory Battery Tester (LBT)
Compact and versatile, our portable desktop solution integrates Arbin's advanced testing features.
LBTS-Cell Tester
Arbin's next generation of multi-function solutions for a full range of cell testing applications.
RBT-Cell Tester
High current cell testing solutions utilizing Arbin's regenerative technology for efficient and reliable testing.
RBT-High Power
Arbin's highest power tester, offering superior energy efficiency, ideal for heavy-duty testing.

Importance of Precision
This plot illustrates the difference between an Arbin battery tester and another leading manufacturer. The first of the two distinct dips in the plot may have been missed using inferior test equipment. While many companies try to sell the same legacy equipment for over a decade, Arbin has been hard at work improving our designs to meet future industry demands.
We learned a lot during our three year ARPA-E project to develop high-current high-precision testers, and have implemented this new technology in our LBT, RBT-Cell, and HPS test equipment series. The HPS ultra-high precision systems represent our premium product, but LBT is superior to other standard testers on the market.
Measurement precision is more critical for long‐term battery testing and long‐term battery projections than control accuracy alone. Most other battery testing systems do not correctly specify their precision and/or have relatively poor precision, which hinder the conclusions drawn from results data. Important trends and electrochemical indicators may remain unnoticed; lost in the measurement noise as illustrated at right.
What Affects Test Equipment Precision
- Resolution of DAC
- Resolution of ADC
- Non-linearity of calibration
- Short-term drift (temperature)
- Long-term drift (material characteristics)
Arbin Test Equipment Improvements
- Higher Resolution
- Improved Software Algorithms
- New Methods of Thermal Management
- New Patented Shunt Design
- New Method of Time Keeping
- New Materials
Ready to Build Your Arbin Battery Testing System?
How to evaluate Battery Testing Equipment
Batteries are a critical component of many products, and energy storage plays a very active role in our lives even outside of the research/industry setting. Therefore, selecting the right battery test equipment is an important decision for companies and the individual researchers who are responsible for producing results, whether they are starting small, or at massive scale.
The expert engineers at Arbin have been advancing the benchmark of “state-of-the-art” battery test equipment for over 30 years. We are defined by innovation, from being the first to apply multiple current ranges on a single test channel to more recently being the only company to offer true high-precision testing for high current applications, and supporting “Turbo Mode” with smart battery modules. We continue to learn from our industry partners and work with them on key technology breakthroughs.

The following report shares some of this knowledge using plain terminology and illustrations. Here are five key topics to consider when choosing battery test equipment:
1. Hardware – Specifications & Quality of Materials
2. Software – Usability and Features
3. Data – Logging, Management, and Analysis
4. Options – Auxiliary Features and Accessories
5. Support – Product Safety and Support
Submit a Support Request Online
We're staying here to hear you
Support Request
"*" indicates required fields